Bleeding Gums
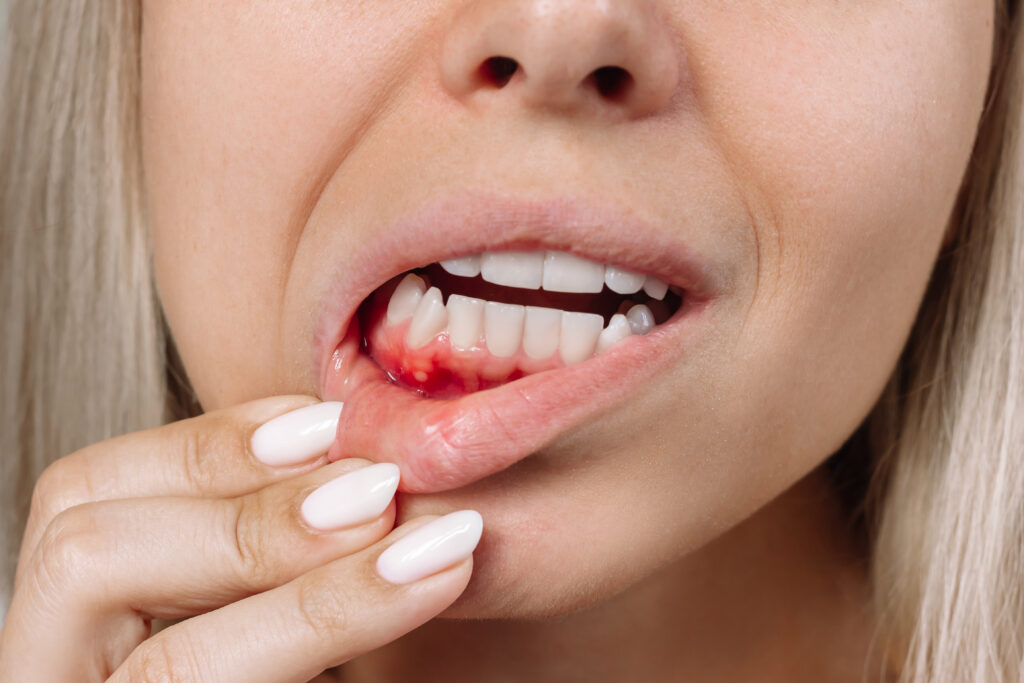
Periodontitis represents an advanced and more severe stage of gum disease, characterized by inflammation and irreversible damage to the gums and supporting structures of the teeth. This condition arises when untreated gingivitis progresses, allowing plaque to spread and grow beneath the gumline, triggering an inflammatory response from the body’s immune system.
One of the significant hallmarks of periodontitis is the formation of pockets between the gums and teeth, causing the gums to pull away and recede. As the disease progresses, these pockets deepen, harboring more bacteria and plaque. Consequently, the body’s immune response and the toxins produced by bacteria start to break down the bone and connective tissues that hold the teeth in place.
Symptoms of periodontitis can include gum recession, exposing more of the tooth’s root, resulting in tooth sensitivity to hot and cold temperatures. Persistent bad breath (halitosis) often accompanies periodontitis due to bacterial infection. Teeth might feel loose or start shifting in their positions, leading to changes in bite alignment. Gum bleeding, especially while brushing or eating, may also occur.
Diagnosis:
• Probing: Measures pocket depths; deeper pockets indicate advanced gum disease.
• X-rays: Assess bone loss and detect underlying issues.
• Clinical Examination: Dentists check for gum recession, tooth mobility, and signs of infection.
Solutions:
• Scaling and Root Planing: Deep cleaning to remove plaque and calculus from below the gumline, promoting gum healing.
• Antibiotic Therapy: Medications in the form of mouth rinses, gels, or pills to control bacterial growth.
• Gum Surgery: Procedures like flap surgery, bone grafts, or tissue regeneration to restore damaged tissues and bone.
• Laser Periodontal Therapy: Laser treatments target and remove infected tissue, aiding in gum healing.
Moreover, diligent oral hygiene practices, including proper brushing, flossing, and regular professional cleanings, become imperative in managing and preventing the progression of periodontitis. Without proper management, advanced periodontitis can lead to tooth loss and impact overall oral health and systemic well-being.
Understanding the symptoms and severity of periodontitis enables individuals to seek timely professional care, undergo appropriate treatments, and adopt preventive measures to preserve gum health and prevent tooth loss.


