Cavities
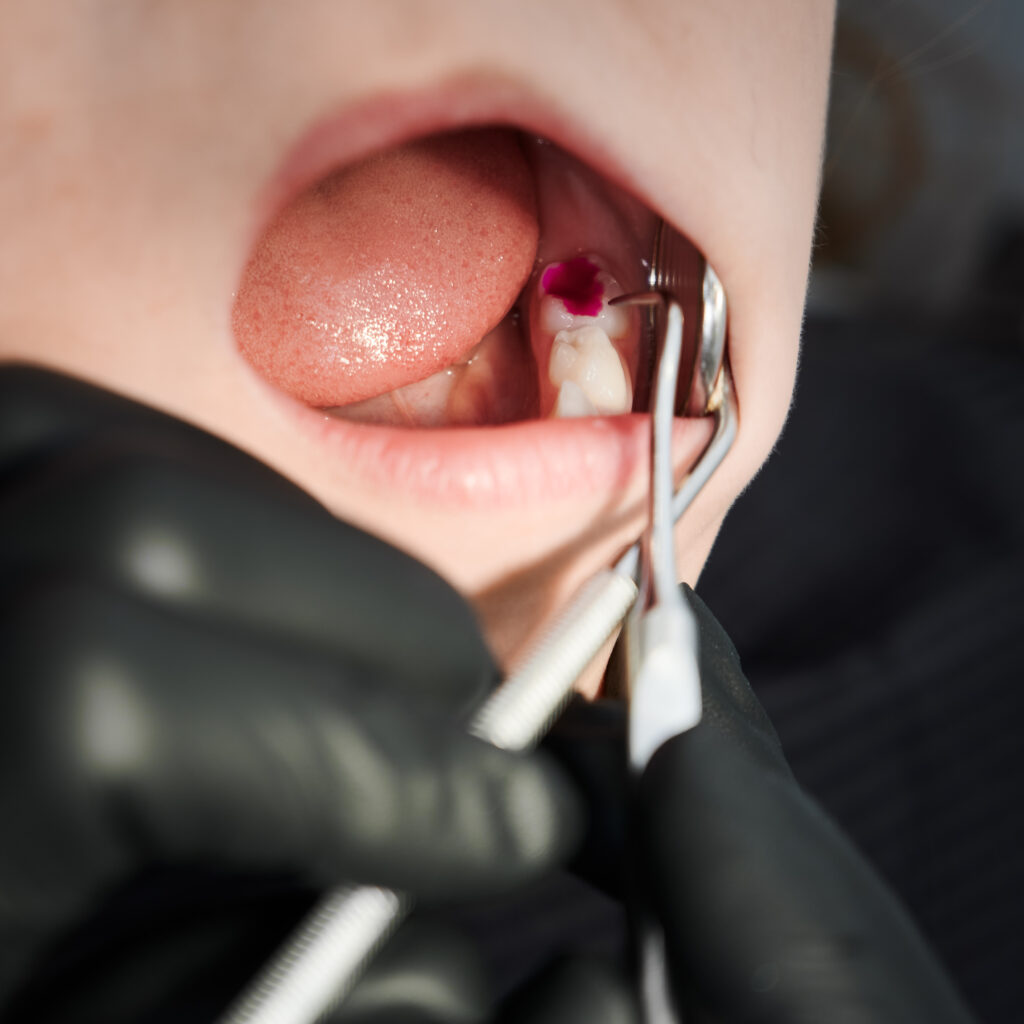
Cavities, also known as dental caries or tooth decay, are one of the most prevalent oral health issues globally. They result from the demineralization of tooth enamel caused by acids produced by bacterial plaque. Cavities often start as small, barely noticeable lesions on the tooth surface and gradually progress into larger, more significant areas of decay.
Symptoms of cavities can vary depending on the stage of decay. Initially, cavities might not exhibit noticeable symptoms. As decay progresses, individuals may experience increased tooth sensitivity to hot, cold, sweet, or acidic foods. Persistent toothaches or spontaneous pain might occur, especially when consuming sugary items or while chewing. Visible holes, pits, or dark spots on the tooth surface indicate the presence of cavities.
Several factors contribute to cavity formation, including poor oral hygiene habits, frequent consumption of sugary or acidic foods and beverages, inadequate fluoride exposure.
Bacteria feed on sugars, producing acids that weaken the enamel, leading to the formation of cavities.
Diagnosis:
- Visual Examination: Dentists look for visible signs of decay or discoloration.
- X-rays: Detect cavities between teeth or under existing fillings.
- Dental Explorer: Used to probe and detect soft areas on tooth surfaces.
Solutions:
- Dental Fillings: Removal of decayed portions and filling cavities with suitable materials.
- Preventive Care: Regular dental check-ups, fluoride treatments, and proper oral hygiene.
- Sealants: Protective coatings applied to prevent cavity formation in vulnerable areas.
- Healthy Diet and Habits: Reducing sugary foods and beverages to minimize cavity risk.
Prevention of cavities involves adopting good oral hygiene practices. Brushing teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily, and using mouthwash help remove plaque and prevent acid buildup. A balanced diet low in sugars and acids reduces the risk of decay. Fluoride treatments and dental sealants applied by dental professionals help strengthen enamel and protect teeth from decay.
Regular dental check-ups every six months allow for early detection and intervention, enabling dentists to address cavities before they progress further and cause more significant damage to the teeth.
Educating individuals about the causes of cavities, the importance of preventive measures, and regular dental visits empowers them to take proactive steps in maintaining optimal oral health and preventing the development of cavities.


