Wisdom Tooth Pain
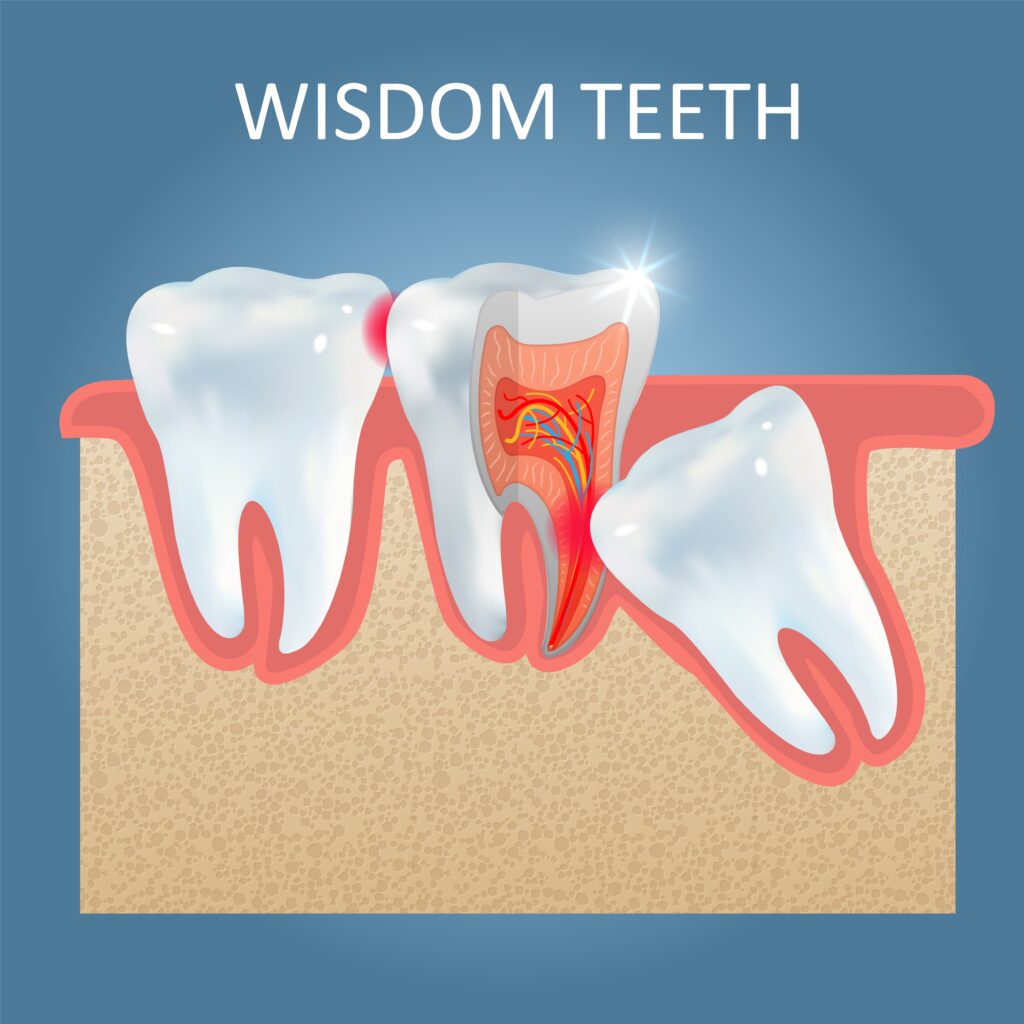
Wisdom teeth, also known as third molars, are the last set of molars that typically emerge in late adolescence or early adulthood. When there is insufficient space in the mouth for these teeth to fully emerge or develop properly, they can become impacted, meaning they are unable to fully erupt through the gums.
Symptoms of impacted wisdom teeth can include pain, swelling, or tenderness in the back of the mouth or jaw, particularly where the affected tooth is located. Individuals might experience difficulty opening their mouths or discomfort while chewing. Impacted wisdom teeth can also lead to gum swelling or infection in the surrounding tissues.
Several factors contribute to the impaction of wisdom teeth, including inadequate space in the jaw, the angle at which the teeth are growing, or obstruction by neighboring teeth or bone. Impacted wisdom teeth can lead to oral health complications such as infection, damage to neighboring teeth, or cyst formation around the impacted tooth.
Diagnosis:
- Clinical Examination: Dentists check for swelling, redness, or signs of infection.
- X-rays: Assess the position and impact of wisdom teeth.
Solutions:
- Extraction: Surgical removal of impacted wisdom teeth to prevent complications.
- Pain Management: Medications to alleviate pain and swelling.
- Antibiotics: Prescribed for infections associated with impacted wisdom teeth.
- Follow-up Care: Post-operative instructions and monitoring for healing.
Preventive measures for impacted wisdom teeth involve regular dental check-ups and X-rays to monitor the development and position of wisdom teeth. If potential issues are identified early, proactive steps can be taken to manage or remove impacted teeth before they cause complications.
Educating individuals about the signs of impacted wisdom teeth and the importance of regular dental assessments empowers them to seek timely intervention, prevent complications, and maintain optimal oral health.


