Bone Grafting
Strengthening Your Foundation for Dental Health
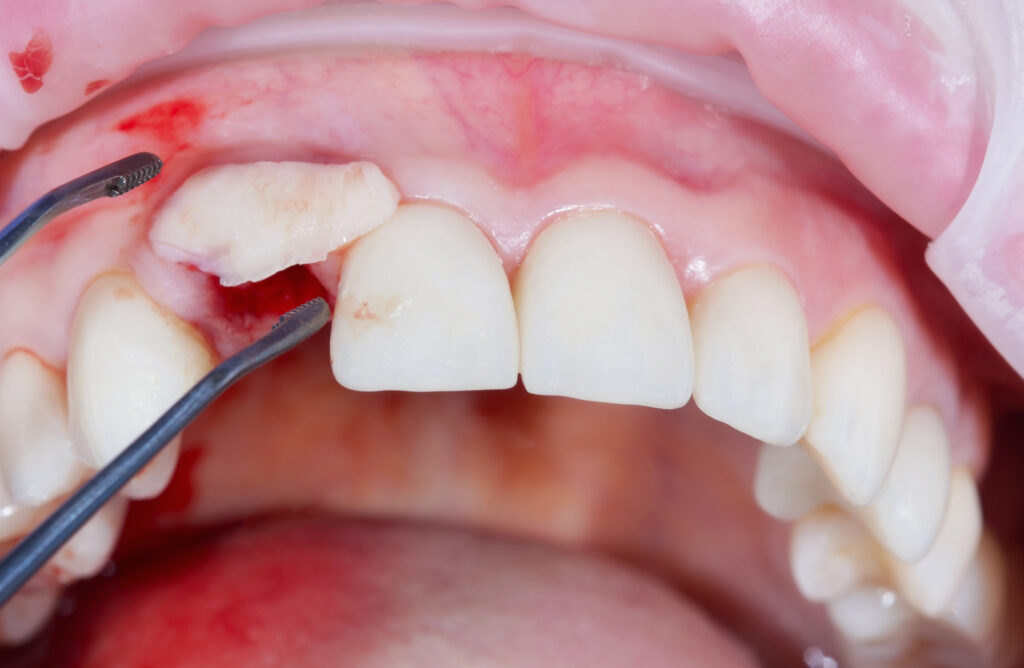
Bone grafting is a specialized dental procedure that plays a crucial role in restoring and strengthening the foundation of your oral health. This surgical technique involves adding bone tissue to areas in the jaw where bone density or volume is insufficient. Bone grafts are commonly performed in preparation for dental implant placement, ensuring implant stability and long-term success. Understanding the importance and process of bone grafting can help you make informed decisions about your dental care.
Why Bone Grafting May Be Necessary:
- Insufficient Bone: Some individuals may not have enough bone volume or density in the jaw to support dental implants. This can be due to factors like tooth loss, periodontal disease, or natural bone resorption.
- Preserving Jaw Structure: Bone grafting is also used to preserve the jawbone after tooth extraction. When a tooth is removed, the surrounding bone may start to deteriorate over time. Grafting helps maintain the bone’s structure and prevents future issues.
The Bone Grafting Process:
Bone grafting is a well-planned and precise procedure that typically involves the following steps:
- Consultation: Your journey begins with a consultation with a dental specialist, often an oral surgeon or periodontist. During this consultation, the specialist will assess your condition, take X-rays or CT scans, and discuss the need for bone grafting.
- Treatment Planning: Once the need for a bone graft is established, a detailed treatment plan is developed. This plan includes selecting the appropriate graft material, which can be sourced from your own body (autograft), a donor (allograft), or synthetic materials.
- Procedure: The bone grafting procedure is usually performed in a dental office or outpatient setting. Local anesthesia is administered to ensure your comfort during the surgery. The graft material is placed in the targeted area, and the surgical site is closed with stitches.
- Healing Period: After the surgery, you’ll enter a healing period during which the graft material integrates with your existing bone. This process is called osseointegration and can take several months.
- Follow-Up: Regular follow-up appointments will be scheduled to monitor your progress. In some cases, a second surgical procedure may be necessary to place dental implants once the graft has fully integrated.
Benefits of Bone Grafting:
- Dental Implant Success: Bone grafting significantly increases the success rate of dental implants. It provides a stable and supportive foundation for the implant to fuse with the jawbone.
- Preservation of Jaw Structure: Bone grafting helps preserve the jaw’s structural integrity, preventing bone loss and associated aesthetic and functional issues.
- Improved Oral Health: By restoring lost bone tissue, bone grafting contributes to overall oral health, making it possible for patients to enjoy the benefits of dental implants, such as improved chewing and speech.
Maintenance and Post-Surgery Care:
After bone grafting surgery, it’s essential to follow your dental specialist’s post-surgery care instructions carefully. This includes managing pain and swelling, maintaining oral hygiene, and attending scheduled follow-up appointments to ensure proper healing and integration.
In summary, bone grafting is a vital procedure that strengthens the foundation of your dental health by restoring bone tissue where it’s needed most. If you’re considering dental implants or have concerns about insufficient bone in your jaw, consult with a dental specialist to explore whether bone grafting is the right option for you. Your specialist will guide you through the process, ensuring a successful outcome and improved oral health.


