Extraction or Root Canal Therapy
Preserving Dental Health through Dental Procedures
In cases of severe tooth decay, infection, or trauma, two common dental procedures may be necessary: tooth extraction and root canal therapy. Both procedures serve specific purposes and are designed to prevent further complications while preserving dental health. Understanding these options can help you make informed decisions about your oral care.
Tooth Extraction:
Tooth extraction, or dental extraction, is the removal of a tooth from its socket in the jawbone. This procedure is typically recommended when a tooth is beyond repair and poses a risk to oral health. Common reasons for tooth extraction include:
- Severe Tooth Decay: When tooth decay is extensive and has compromised a significant portion of the tooth, extraction may be necessary if other treatments are not viable.
- Infection: Untreated dental infections can lead to abscesses, which may necessitate tooth extraction to prevent the spread of infection.
- Trauma: Teeth that are severely damaged due to trauma or accidents may need to be extracted if they cannot be effectively restored.
- Orthodontic Treatment: In some cases, tooth extraction is part of orthodontic treatment plans to create space for proper tooth alignment.
Root Canal Therapy:
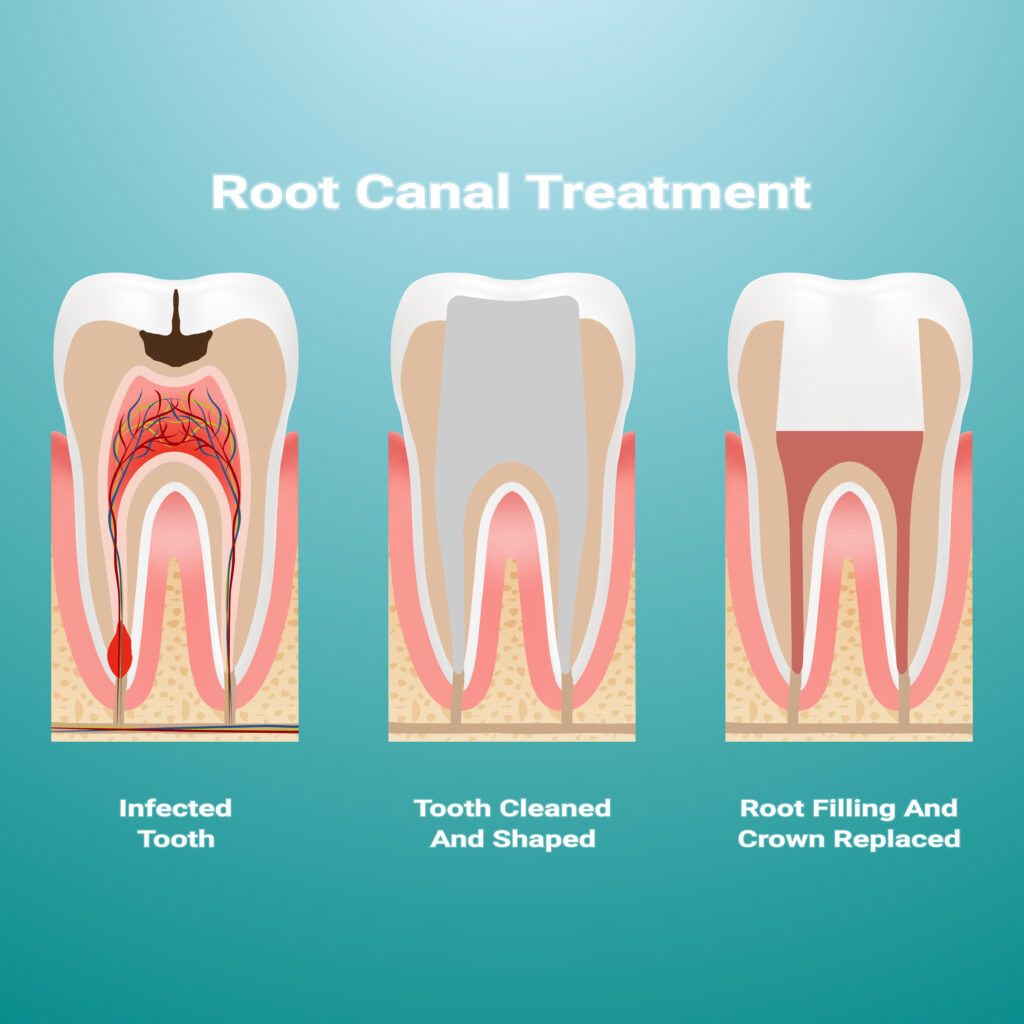
Root canal therapy, often referred to as endodontic treatment, is a procedure performed to save a tooth that is severely infected or has damaged pulp (the innermost part of the tooth). During a root canal, the infected or damaged pulp is removed, and the tooth is cleaned, disinfected, and sealed. Root canal therapy is typically recommended when:
- Tooth Infection: A bacterial infection has reached the pulp, causing pain, swelling, and potential abscess formation.
- Deep Decay: When decay has penetrated deep into the tooth, affecting the pulp, root canal therapy can help preserve the tooth.
- Trauma: Teeth that have experienced significant trauma may require root canal therapy if the pulp is damaged.
The Tooth Extraction Process:
- Assessment: Your dentist will evaluate the tooth’s condition and discuss the need for extraction. X-rays may be taken to assess the tooth and surrounding structures.
- Anesthesia: Local anesthesia is administered to numb the area, ensuring your comfort during the procedure.
- Extraction: Using specialized instruments, the dentist carefully removes the tooth from its socket. In some cases, sutures may be needed to close the extraction site.
- Aftercare: Post-extraction care instructions will be provided, including guidelines for managing any discomfort and promoting healing.
The Root Canal Therapy Process:
- Diagnosis: Your dentist will diagnose the need for root canal therapy based on your symptoms, clinical examination, and X-rays.
- Anesthesia: Local anesthesia is administered to numb the tooth and surrounding area.
- Access and Cleaning: A small access hole is created in the tooth to reach the infected pulp. The infected tissue is removed, and the tooth’s interior is cleaned and disinfected.
- Filling and Sealing: After cleaning, the tooth is filled with a biocompatible material, and a sealing material is used to close the access hole.
- Restoration: In most cases, a crown is placed on the treated tooth to provide strength and protection.
Benefits of Tooth Extraction and Root Canal Therapy:
- Pain Relief: Both procedures aim to alleviate pain and discomfort associated with severe dental issues.
- Preservation: Root canal therapy preserves a tooth that may otherwise need extraction, while extraction removes a problematic tooth to prevent further complications.
- Oral Health: Both procedures contribute to overall oral health by addressing severe dental problems.
Maintenance and Post-Procedure Care:
Following tooth extraction or root canal therapy, following your dentist’s post-procedure care instructions is crucial for a successful recovery. This may include proper oral hygiene, medication use, and any recommended follow-up appointments.
In summary, tooth extraction and root canal therapy are dental procedures designed to address severe dental issues and preserve dental health. If you have concerns about a tooth or are experiencing dental pain, consult with your dentist to discuss the most appropriate treatment option for your specific situation. Your dentist will provide guidance to help you make an informed decision about your oral care.


